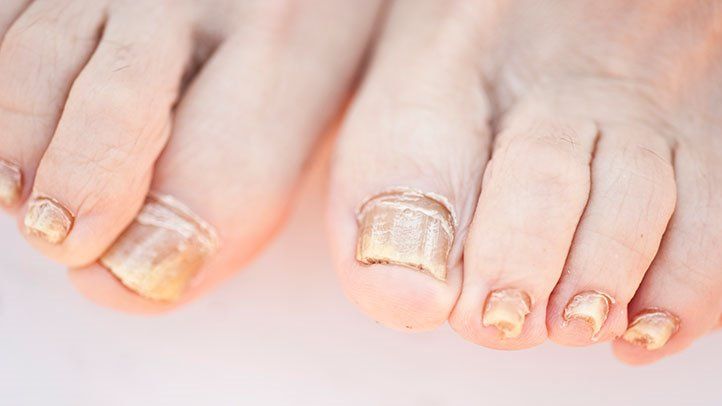
Diabetes is a chronic condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It occurs when the body is unable to produce or use insulin effectively, resulting in high blood sugar levels. One lesser-known complication of diabetes is toenail fungus, which can cause thickened, discolored, and brittle nails. In this article, we’ll explore the connection between diabetes and toenail fungus, including how the two conditions are related and what you can do to prevent and treat toenail fungus if you have diabetes.
Why Are People with Diabetes More Prone to Toenail Fungus?
One of the main reasons why people with diabetes are more prone to toenail fungus is because high blood sugar levels can weaken the immune system. When the immune system is compromised, it becomes less effective at fighting off infections, including fungal infections. This means that people with diabetes are more likely to develop toenail fungus and other types of fungal infections, such as athlete’s foot. Another reason why people with diabetes are more prone to toenail fungus is because they may have poor circulation. High blood sugar levels can damage blood vessels and nerves, leading to reduced blood flow to the feet and toes. This can create an environment that is conducive to the growth of fungi, as the nails and surrounding skin may not receive adequate nutrients and oxygen to stay healthy.
Is Toenail Fungus Contagious?
Toenail fungus is a contagious condition that can spread from person to person, caused by a type of fungus called dermatophytes, which thrive in warm, moist environments such as public swimming pools, locker rooms, and communal showers. If you have diabetes and are in contact with someone who has toenail fungus, you may be at a higher risk of developing the condition. For more information on how to maintain good foot health and prevent toenail fungus, you can explore PureHealth Research.

Preventing and Treating Toenail Fungus in People with Diabetes
If you have diabetes, it’s important to take steps to prevent toenail fungus from developing in the first
place. Some of the things you can do include:
Keeping your feet clean and dry: This means washing your feet with soap and water every day, drying them thoroughly, and applying a moisturizer to prevent dryness.
Trimming your toenails properly: Trim your nails straight across, and avoid cutting them too short or rounding the corners, which can increase the risk of ingrown toenails.
Wearing shoes that fit properly: Choose shoes that are comfortable, breathable, and provide adequate support. Avoid wearing shoes that are too tight or too loose, as this can increase the risk of toenail fungus and other foot problems.
Changing your socks frequently: Wear clean socks every day, and choose socks made from breathable materials such as cotton or wool.
Treatment Options for Toenail Fungus in People with Diabetes
If you do develop toenail fungus, there are several treatments available that can help. These include:
Topical antifungal creams or ointments: These can be applied directly to the affected nail to kill the fungus and promote healthy nail growth.
Oral antifungal medications: These are prescription medications that are taken orally and work by attacking the fungus from the inside out.
Laser therapy: This is a newer treatment option that uses laser energy to kill the fungus without damaging the surrounding tissue. It’s important to talk to your doctor before starting any treatment for toenail fungus, as some medications and therapies may not be safe for people with diabetes.
Conclusion
Toenail fungus is a common condition that can be especially problematic for people with diabetes. High blood sugar levels and poor circulation can make it more difficult for the body to fight off fungal infections, which can lead to thicker, discolored, and brittle nails. By taking proactive steps to prevent and treat toenail fungus, such as following good foot hygiene practices and seeking appropriate medical care, people with diabetes can maintain good foot health and reduce their risk of complications associated with this condition.